An Introduction
Guar Gum is the ground endosperm of the seed of the plant Cyamopsis tetragonolobus. It has been widely cultivated for centuries in India, for both animal and human consumption, and today India meets nearly 85% of the worldwide demand for Guar Gum.
Guar is primarily grown in the states of Rajasthan, Haryana and Gujarat and to a very small extent in the states of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh. However due to the recent rise in demand for Guar Gum, other Indian states such as Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh have also started experimenting with Guar cultivation.
The Guar crop is sown after the first rains in June / July and is harvested after approximately 3 months. Guar is a hardy, drought-resistant plant and requires 3 to 4 moderate rains at intervals of 15 to 20 days.
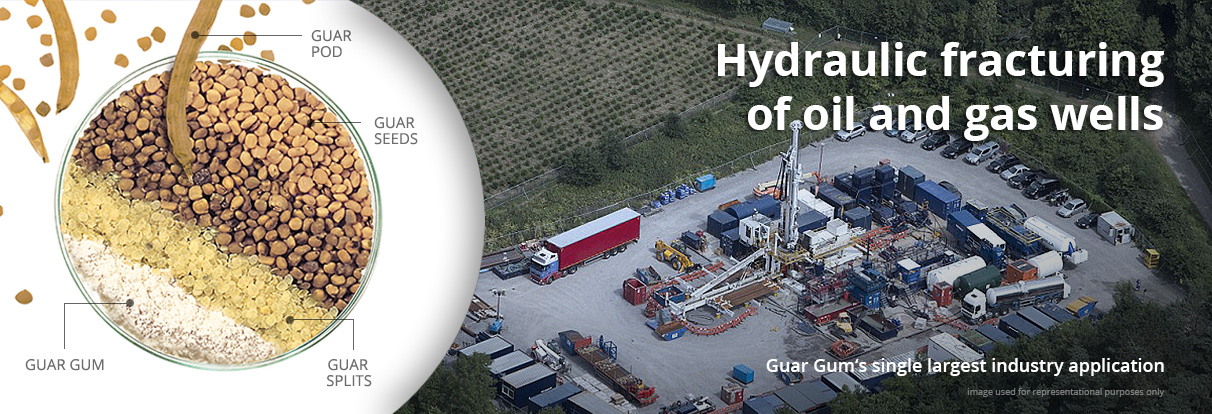
The Guar plant sprouts bean-like pods that are 5-10 cms long and contains 8-10 seeds. Guar seeds are about 3 mm to 5 mm in diameter and are dicotyledonous i.e. they have two endosperm halves. Also known as Guar Splits, the endosperm halves are separated from the germ and hull using a combination of thermal and mechanical processes. Guar Splits are then milled to produce Guar Gum powder.
Physical and Chemical Characteristics
Guar Gum is a creamish-white bland-tasting powder that is almost odourless. It disperses readily in hot or cold water to form a viscous pseudoplastic sol.
Guar Gum is a polysaccharide. The galactomannan molecule is composed of a long straight chain of D-mannopyranose units with single membered side chains of D-galactopyranose units. The molecular weight of Guar Gum is estimated at between 200,000 and 250,000 Dalton.
Gel formation
Cohesive structural gels can be formed by adding borate ions, which act as cross-linking agents, to a hydrated alkaline Guar Gum solution.
Compatibility with other hydrocolloids
Guar Gum is compatible with most other hydrocolloids and water soluble polymers such as Agar, Arabic, Carrageenan, Karaya, Locust Bean Gum, Pectin, Propylene Glycol Alginate, Sodium Alginate, Tragacanth, Methylcellulose, CMC and Xanthan. It is also compatible with raw starches, most modified starches and many water soluble proteins.
Applications
Hydraulic Fracturing
Oil Well Drilling
Dairy
Bakery
Meat
Instant Noodles
Pet Food
Mining
Water Gel Explosives
Tobacco
Today the largest user of Guar Gum in the world is the oil & gas industry.
Hydraulic Fracturing: Guar Gum and its derivatives are used in the fracturing of oil and gas wells because of their ability to thicken water effectively at low concentration. They carry the sand or proppants needed to keep the fracture from closing when the pressure is released. They are reliable polymers that will hydrate in field waters under many conditions.
Guar Gum and its derivatives are used to formulate different types of fracturing fluids – linear gels, cross-linked gels and organometallic crosslinked fluids – which form the core of the hydraulic fracturing process.
Drilling: Guar Gum is used to control flow and as a protective colloid in oil well drilling muds.
Regulatory Information
| CAS No. | 9000-30-0 |
| FAO / WHO | Recognized as a Food Additive |
| USA | Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) as per Code of Federal Regulations (CFR 21) |
| EEC | E 412 |
| HS Code | 13023230 |
Guar Gum Grades from Premcem
Fast Hydrating Guar Gum
| Grade | Viscosity @ 3 min | Free Flowing |
|---|---|---|
| PFHG-35 | 35 cps minimum | No |
| PFHG-37 | 37 cps minimum | No |
| PFHG-40 | 40 cps minimum | No |
| PFHG-35F | 35 cps minimum | Yes |
Hydration Viscosities for a 40 lb system in 2% KCl using a Fann 35 with R1B1 at 511s¯¹
Regular Guar Gum – Food and Industrial
| Particle Size | Viscosity Range |
|---|---|
| 60 mesh | 300 cps – 2500 cps |
| 100 mesh | 1000 cps – 4500 cps |
| 200 mesh | 2000 cps – 7500 cps |
Grades can also be customized as per customer’s requirement.